 k9s is a lightweight tool that provides a powerful and user-friendly interface for managing and monitoring Kubernetes clusters. It makes it easy to list, filter, and view resources, as well as describe, edit, scale, and delete them. Plus, you can use k9s to port forward to pods, benchmark them, and check resources with the same name across different API groups. You can even customize log settings and install plugins to add new functionality.
k9s is a lightweight tool that provides a powerful and user-friendly interface for managing and monitoring Kubernetes clusters. It makes it easy to list, filter, and view resources, as well as describe, edit, scale, and delete them. Plus, you can use k9s to port forward to pods, benchmark them, and check resources with the same name across different API groups. You can even customize log settings and install plugins to add new functionality.
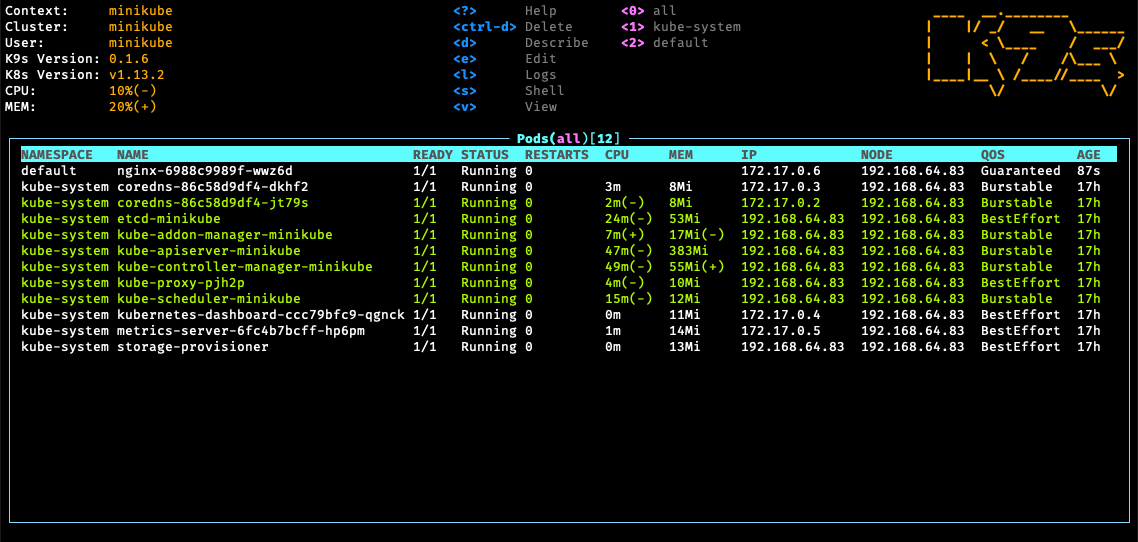
Start k9s
# Use default kubeconfig
$ k9s
# Use non-default kubeconfig
$ k9s --kubeconfig /path/to/kubeconfig
# Use non-default context
$ k9s --context fooctx
# Readonly
$ k9s --readonly
# Check info (locations for configuration, logs, screen dumps)
$ k9s info
Using k9s
List Resources
List a specific resource:
:<resource>: list Resources, e.g. :pod to list all pods.
:<resource> <namespace>: list Resources in a given namespace.
List all available resources:
:aliases or Ctrl-a: list all available aliases and resources.
:crd: list all CRDs.
Filter
/<filter>: regex filter.
/!<filter>: inverse regex filter.
/-l <label>: filter by labels.
/-f <filter>: fuzzy match.
Choose namespace
Type :namespace, select the desired namespace by up or down key, press Enter to select.
Choose context
:ctx: list ctx, then select from the list.
:ctx <context>: switch to the specified context.
Show Decrypted Secrets
Type :secrets to list the secrets, then
xto decrypt the secret.Escto leave the decrypted display.
Key mapping
- move up and down without moving your right hand:
j: down.k: up.
SPACE: select multiple lines (e.g. then Ctrl-d to delete)y: yaml.d: describe.v: view.e: edit.l: logs.w: wrap.r: auto-refresh.s: scale the number of replicas.x: decode a Secret.-
f: full screen. Tip: enter full screen mode before copying, to avoidin copied text. Ctrl-d: delete.Ctrl-k: kill (no confirmation).Ctrl-w: toggle wide columns. (Equivalent to kubectl … -o wide)Ctrl-z: toggle error stateCtrl-e: hide header.Ctrl-s: save output (e.g. the YAML) to disk.Ctrl-l: rollback.
Sort by Column
Shift-c: sorts by CPU.Shift-m: sorts by MEMORY.Shift-s: sorts by STATUS.Shift-n: sorts by name;Shift-o: sorts by node;Shift-i: sorts by IP address;Shift-a: sorts by container age;Shift-t: sorts by number of restarts;Shift-r: sorts by pod readiness;
Helm
:helm: show helm releases.:helm NAMESPACE: show releases in a specific namespace.
XRay View
:xray RESOURCE, e.g.:xray deploy.
Pulse View
:pulse: displays general information about the Kubernetes cluster.
Popeye View
:popeyeorpop: checks all resources for conformity with the correctness criteria and displays the resulting “rating” with explanations. https://popeyecli.io
Show Disk Files
:dir /path
E.g. :dir /tmp will show your /tmp folder on local disk. One common use case: Ctrl-s to save a yaml, then find it in :dir /tmp/k9s-screens-root, find the file, press e to edit and a to apply.
Quit
Esc: Bails out of view/command/filter mode.:qorCtrl-c: quit k9s.
Tips
Monitor what’s going on:
:event (or ev): see the stream of events.:pod:job
k9s Warnings
E.g. memory level warning, to check CPU/Memory usage:
kubectl top nodes
kubectl top pods
Benchmark
k9s includes a basic HTTP load generator.
To enable it, you have to configure port forwarding in the pod. Select the pod and press SHIFT + f, go to the port-forward menu (using the pf alias).
After selecting the port and hitting CTRL + b, the benchmark would start. Its results are saved in /tmp for subsequent analysis.
To change the configuration of the benchmark, create the $HOME/.k9s/bench-<my_context>.yml file (unique for each cluster).
Configure k9s
Note that all YAML files in the .k9s directory must have the .yml extension (.yaml doesn’t work).
$HOME/.k9s/views.yml: customize the column view for resource lists.$HOME/.k9s/plugin.yml: manage plugins.$XDG_CONFIG_HOME/k9s/config.yml: k9s config.$XDG_CONFIG_HOME/k9s/alias.yml: define your own alias.$XDG_CONFIG_HOME/k9s/hotkey.yml: define your own hotkeys.$XDG_CONFIG_HOME/k9s/plugin.yml: manage plugins.
Check Resources with the Same Name in Different API Groups
e.g. Cluster may be found in different api groups, like cluster.x-k8s.io or clusterregistry.k8s.io or baremetal.cluster.gke.io.
apiVersion: cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: clusterregistry.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: baremetal.cluster.gke.io/v1
kind: Cluster
Use apiVersion/kind (i.e. Group/Version/kind) instead of just kind to check the API of a specific group.
:cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3/clusters:clusterregistry.k8s.io/v1alpha1/clusters:baremetal.cluster.gke.io/v1/clusters
Change log setting
Change ~/.config/k9s/config.yml:
logger:
tail: 500
buffer: 5000
sinceSeconds: -1
Plugins
https://github.com/derailed/k9s/tree/master/plugins
Install
# Go
$ go install github.com/derailed/k9s@latest
# Homebrew / LinuxBrew
$ brew install derailed/k9s/k9s
# MacPort
sudo port install k9s
# Snap
sudo snap install k9s
# PacMan
pacman -S k9s
# Windows: scoop
scoop install k9s
# Windows: chocolatey
choco install k9s
Official Website: https://k9scli.io/